 |
PVCAM
3.9.x
Programmable Virtual Camera Access Method library
|
 |
PVCAM
3.9.x
Programmable Virtual Camera Access Method library
|
Rolling Shutter and Global Shutter are the two primary operating modes of sCMOS image sensors. In Global Shutter readout, a global charge clearing mechanism begins the exposure period for all pixels. Each pixel accumulates signal charge until the exposure period ends. At this point, the accumulated charge is transferred and converted to voltage in each pixel output node, ending the exposure.
The advantage of the Global Shutter approach is that all the pixels are exposed at the same instant in time - an important attribute when imaging fast moving objects. The acquisition consists of two phases - an active image accumulation phase and a subsequent readout phase. As the phases are not overlapped in time, the maximum achievable frame rate is lower.
In Rolling shutter readout, exposure and readout are overlapped. This is accomplished by reading one row while exposing all of the other rows - the row being digitized "rolls" through the sensor.
For Prime 95B camera, the time to digitize a single row is 20us, and consequently the delay between the start of exposure between two adjacent rows is approximately 9.6us. Digitizing 1200 rows of pixels, the time delay from the top to the middle of the sensor is approximately 24 ms. Since readout and exposure are overlapped, the sensor achieves the maximum frame rate of 40fps. In 12-bit mode, as two rows are read out simultaneously, the row time is effectively halved to 10us, providing an increased maximum frame rate of 80fps.
The graphic below depicts the time delay between each row of pixels in a rolling shutter readout mode with an sCMOS camera.
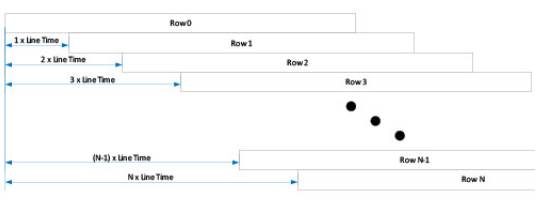
The downside of Rolling Shutter readout is that changes in the scene on similar time scales distort the image as each row is sampled at different time. This is the well known "rubber band" effect which can also appear in fluorescence microscopy as shaded illumination when rapidly changing wavelengths.
To maintain the benefit of Rolling Shutter readout and eliminate rolling shutter artifacts, external illumination can be gated on when all rows are being exposed simultaneously, and off during the readout phase. This external triggering mode used in combination with high speed light sources (lasers, LEDs) achieves a pseudo global shutter effect. This triggering mode is described in the device synchronization section of this manual.